A new, comprehensive analysis of satellite data finds that majority of glaciers on the landmass have retreated significantly.
The Greenland Ice Sheet has shed about one-fifth more ice mass in the past four decades than previously estimated, researchers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California reported in a new paper. The majority of glaciers on the landmass have retreated significantly, and icebergs are falling into the ocean at an accelerating rate. This additional ice loss has had only an indirect impact on sea levels, but could hold implications for ocean circulation in the future.
Published in Nature on Jan. 17, the analysis offers a comprehensive look at retreat around the edges of the entire ice sheet from 1985 to 2022, drawing from nearly a quarter million pieces of satellite data on glacier positions. Of the 207 glaciers in the study, 179 retreated significantly since 1985, 27 held steady, and one advanced slightly.
Most of the ice loss came from below sea level, in fjords on Greenland’s periphery. Once occupied by ancient glacial ice, many of these deep coastal valleys have filled with seawater – meaning the ice that broke off made little net contribution to sea level. But the loss likely accelerated the movement of ice flowing down from higher elevations, which in turn added to sea level rise.
“When the ice at the end of a glacier calves and retreats, it’s like pulling the plug out of the fjord, which lets ice drain into the ocean faster,” said Chad Greene, a glacier scientist at JPL and the study’s lead author.
Accounting for Glacial Retreat
For decades researchers have studied the Greenland Ice Sheet’s direct contributions to global sea level rise through ice flow and melting. Scientists participating in the international Ice sheet Mass Balance Inter-comparison Exercise (IMBIE) estimated that the ice sheet had lost 5,390 billion tons (4,890 billion metric tons) between 1992 and 2020, adding about 0.531 inches (13.5 millimeters) to global mean sea level, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
But the IMBIE measurements do not account for ice lost due to the retreat of terminal glaciers along the edges of Greenland. (These glacier edges were already in the water, whether submerged or floating.) The new study quantifies this amount: For the 1985 to 2022 period in the new paper, the ice sheet was estimated to have lost about 1,140 billion tons (1,034 billion metric tons) – 21% more mass lost than in the IMBIE assessment.
Although it doesn’t add to sea levels, the additional ice represents a significant influx of fresh water to the ocean. Recent studies have suggested that changes in the salinity of the North Atlantic Ocean from melting icebergs could weaken the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, part of the global “conveyor belt” of currents that transport heat and salt around the ocean. This could influence weather patterns worldwide, as well as affect ecosystems, the authors said.
A Comprehensive View of Glacial Retreat
Icebergs have tumbled from Greenland’s glaciers for thousands of years as part of a natural cycle that typically balanced glacier growth in the winter with melting and retreat in the summer. The new study finds that ice retreat has far outpaced growth throughout the 21st century.
The researchers also found that Greenland’s ice extent remained relatively steady from 1985 to 2000, then started a marked recession that continues to this day.
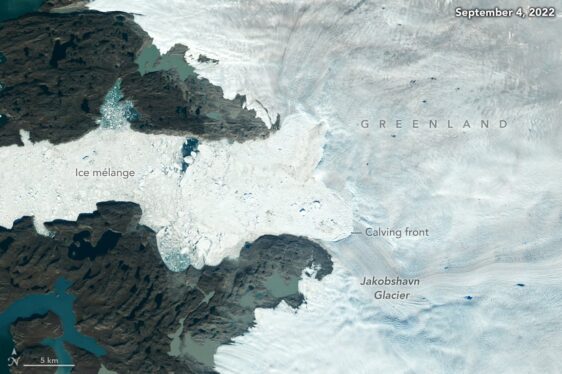
The data showed a glacier in northeast Greenland called Zachariae Isstrom lost the most ice, dropping 176 billion tons (160 billion metric tons) of mass due to retreat. It was followed by Jakobshavn Isbrae on the western coast, which lost an estimated 97 billion tons (88 billion metric tons), and Humboldt Gletscher in the northwest, which lost 96 billion tons (87 billion metric tons).
Only one glacier, Qajuuttap Sermia in southern Greenland, experienced any growth over the study period, but its gains were too small to offset the losses from other glaciers.
The researchers also found that glaciers with the largest seasonal fluctuations in the position of their ice front experienced the greatest overall retreat. The correlation suggests the glaciers that are most sensitive to warming each summer will be most impacted by climate change in the coming decades.
The discovery of a large-scale pattern of glacier retreat and its link to glacier sensitivity on seasonal time scales was the result of a big-data synthesis that looks at all parts of the ice sheet over time, said JPL cryosphere scientist Alex Gardner, a co-author of the paper. Scientists drew from five publicly available datasets that cumulatively tracked the month-to-month positions of 236,328 glacier edges as detected, either manually or by computer algorithms, in images collected by optical and radar satellites.
“Previously, we had bits and pieces – lots of local studies,” Gardner said. “But what this study offers is a systematic and comprehensive view that has led to some pretty significant insights that we didn’t have about the ice sheet before.”
News Media Contacts
Andrew Wang / Jane J. Lee
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-379-6874 / 818-354-0307
andrew.wang@jpl.nasa.gov / jane.j.lee@jpl.nasa.gov
2024-002