This article is for students grades 5-8.
The Sun is the star of our solar system. Its gravity holds Earth and our planetary neighbors in its orbit. At 865,000 miles (1.4 million km) in diameter, it’s the largest object in our solar system. On Earth, its influence is felt in our weather, seasons, climate, and more. Let’s learn about our dynamic star and its connections to life on Earth.
What is the Sun, and what is it made of?
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star. It is approximately 4.5 billion years old and is in its “main sequence” phase. This means it is partway through its lifecycle with a few billion more years ahead of it.
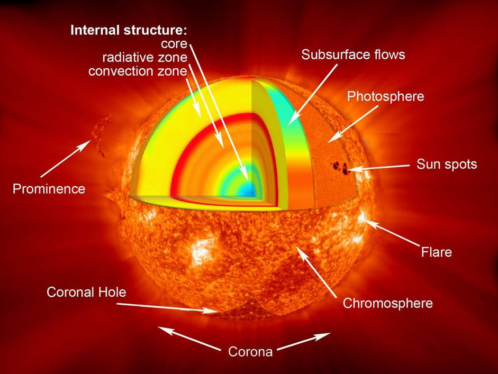
The Sun is made of hydrogen and helium gases. At its core, hydrogen is fused to form helium. This nuclear reaction creates the Sun’s heat and light. That energy moves outward through the Sun’s radiative zone and convective zone. It then reaches the Sun’s visible surface and lower atmosphere, called the photosphere. Above the photosphere lies the chromosphere, which forms the Sun’s middle atmosphere, and beyond that is the corona, the Sun’s outermost atmosphere.
What is the solar cycle?
The Sun goes through a pattern of magnetic activity known as the solar cycle. During each cycle, the Sun experiences a very active period called “solar maximum” and a less active period called “solar minimum.”
During solar maximum, increased magnetic activity creates sunspots. These appear as darker, cooler spots on the Sun’s surface. The more sunspots we can see, the more active the Sun is.
The solar cycle begins at solar minimum, peaks at solar maximum, and then returns to solar minimum. This cycle is driven by the Sun’s magnetic polarity, which flips – north becomes south, and vice versa – every 11 years. It takes two cycles – or 22 years – to complete the full magnetic cycle where the poles return to their original positions.
Wait. The Sun’s magnetic poles can flip??
Yes! Like Earth, the Sun has north and south magnetic poles. But unlike Earth, the Sun’s poles flip regularly. Each 11-year solar cycle is marked by the flipping of the Sun’s poles. The increased magnetic activity during solar maximum makes the north and south poles less defined. As the cycle moves back to solar minimum, the polarization of the poles returns – with flipped polarity.
What is space weather?
Space weather includes phenomena such as solar wind, solar storms, and solar flares. When space weather conditions are calm, there may be little noticeable effect on Earth. But when the Sun is more active, space weather has real impacts on Earth and in space.
Let’s explore these phenomena and how they affect our planet.
What is solar wind?
Solar wind is a stream of charged particles that flow outward from the Sun’s corona. It extends far beyond the orbit of the planets in our solar system. When solar wind reaches Earth, its charged particles interact with Earth’s magnetic field. This causes colorful streams of moving light at Earth’s north and south poles called aurora.
What are solar storms, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections?
The Sun’s magnetic fields are a tangle of constant motion. These fields twist and stretch to the point that they snap and reconnect. When this magnetic reconnection occurs, it releases a burst of energy that can cause a solar storm.
Solar storms can include phenomena such as solar flares or coronal mass ejections. They happen more frequently around the solar maximum of the Sun’s cycle. A solar flare is an intense burst of light and energy from the Sun’s surface. Solar flares tend to happen near sunspots where the Sun’s magnetic fields are strongest. A coronal mass ejection is a massive cloud of material flowing outward from the Sun. These can occur on their own or along with solar flares.
How do these phenomena affect Earth?
When a solar storm erupts towards Earth, our atmosphere and magnetic field protect us from significant harm. However, some impacts are possible, both on Earth and in space. For example, strong solar storms can cause power outages and radio blackouts. GPS signals can be disrupted. Satellite electronics can be affected. And astronauts working outside of the International Space Station could be exposed to dangerous radiation. NASA monitors and forecasts space weather to protect the safety and health of astronauts and spacecraft.
Learn more about the Sun
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe launched in 2018 on the first-ever mission to fly into the Sun’s corona. Since its first pass through the corona in 2021, every orbit has brought it closer to the Sun. On Dec. 24, 2024, it makes the first of its three final, closest solar approaches of its primary mission. Test your knowledge with NASA’s new quiz, Kahoot! Parker Solar Probe trivia.
Visit these resources for more details about the Sun:
- https://science.nasa.gov/sun/facts/
- https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/all-about-the-sun/en/
- https://science.nasa.gov/exoplanets/stars/
https://www.nasa.gov/learning-resources/for-kids-and-students/how-does-the-sun-behave-grades-5-8/










Leave a Reply